Utilities Business Intelligence has emerged as a significant game-changer in a rapidly evolving utility industry. As data analytics and advanced technologies continue to advance, they bring unprecedented opportunities for enhancing operational efficiency and delivering superior customer service. This comprehensive guide aims to unveil the transformative power of Utilities Business Intelligence, highlighting how it is revolutionizing the way utility companies operate. Expect to discover invaluable insights into harnessing data-driven strategies that streamline operations and drive growth and customer satisfaction. Whether you’re a utility industry professional or a business intelligence enthusiast, this guide covers you.
What is Utilities Business Intelligence?
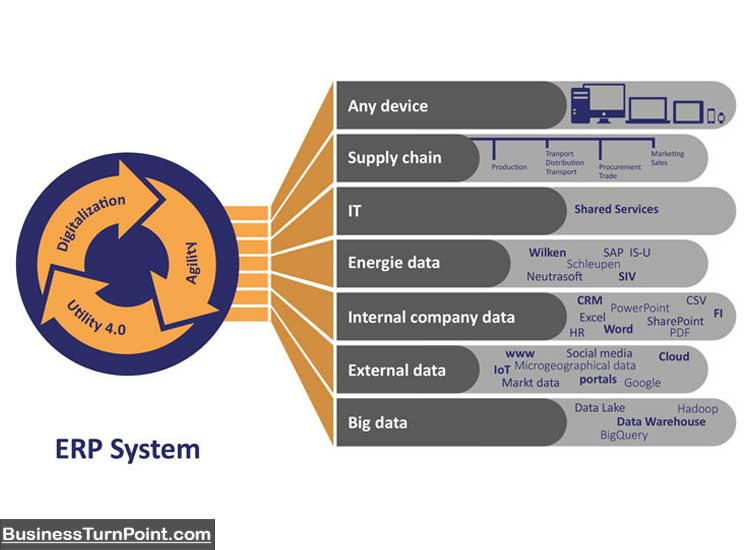
Utilities Business Intelligence (UBI) is a powerful tool for the utility sector. It aims to make operations more efficient by turning data into actionable insights. UBI helps utility companies survive and thrive in a data-driven world by leveraging various data analytics and reporting tools.
Definition and Core Components
Utilities Business Intelligence uses technologies, tools, and practices to collect, integrate, analyze, and present business data. The goal is to support better decision-making within the organization. Key components include:
- Data Collection: Gathering information from various sources such as smart meters, customer feedback, and operational systems.
- Data Integration: Combining data from multiple sources creates a unified view.
- Data Analysis: Using analytical tools to examine data and identify patterns or trends.
- Data Visualization: Presenting data in charts, graphs, and dashboards to make it easier to understand.
Functions and Applications
Utilities Business Intelligence serves multiple crucial functions:
- Performance Monitoring: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) to ensure operations run smoothly.
- Predictive Maintenance: Use historical data to predict equipment failures before they happen.
- Customer Insights: Understand customer behavior and preferences to improve service delivery.
- Regulatory Compliance: Monitor compliance metrics by ensuring all operations meet local and national regulations.
Integration with Other Systems
UBI doesn’t operate in isolation. It integrates seamlessly with other systems within the utility sector:
- Geographic Information System (GIS): Enhances spatial data analysis for better asset management.
- Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) Systems: Monitors and controls physical processes to provide real-time data.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: Connects customer data to operational data for a comprehensive view of customer interactions.
Benefits of Utilities Business Intelligence
Implementing UBI offers several benefits:
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Utilities can streamline operations and reduce waste by analyzing data.
- Enhanced Decision-Making: UBI provides the insights needed to make more informed decisions quickly.
- Better Customer Satisfaction: Understanding customer needs enables personalized service and quicker resolution of issues.
- Cost Savings: Predictive analytics can reduce maintenance costs and prevent costly outages.
For deeper insights into how UBI can specifically benefit utility companies, check out this comprehensive guide on utilities business intelligence.
Incorporating Utilities Business Intelligence helps utility companies navigate the complexities of modern energy demands, ensuring they meet customer needs efficiently and effectively. This transformative tool is integral to the future of utility management, driving smarter, data-informed decisions that power progress.
Stay tuned as we explore more aspects of UBI and how it is revolutionizing the utility sector.
The Importance of Data Analytics in Utilities
In today’s digital age, data analytics is a crucial driver for innovation and efficiency in the utility industry. By leveraging large volumes of data, utilities can optimize their operations, improve customer satisfaction, and make informed decisions contributing to better resource management and cost savings.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
Data analytics is a potent tool for boosting operational efficiency in the utilities sector. Here’s why:
- Optimizing Operations: Utility companies can monitor their systems in real-time by analyzing data from various sources, such as smart meters and sensors. This helps identify inefficiencies and areas that need attention before they escalate into bigger problems.
- Reducing Costs: Analytics can pinpoint wasteful practices and help implement cost-saving measures. For instance, utilizing predictive analytics allows utilities to anticipate maintenance needs and avoid costly outages and repairs.
- Enhancing Resource Management: Data analytics provides a clear picture of resource usage, enabling utilities to manage assets more effectively. This includes the intelligent distribution of electricity, water, or gas, which reduces the strain on resources and minimizes losses.
These benefits collectively lead to a more streamlined operation, saving time and money. Check out this detailed article on how utilities leverage data analytics for deeper insights.
Improving Customer Satisfaction
Data analytics is not just about improving operations but also understanding and serving customers better. Here’s how:
- Understanding Customer Needs: Utilities can gain insights into usage patterns and preferences by collecting and analyzing customer data. This enables them to offer personalized services and solutions tailored to individual customer needs.
- Enhancing Customer Service: Analytics can help predict when customers might face service issues or need support, allowing for proactive service strategies. For example, if data indicates a potential power outage, the utility can inform affected customers in advance and prepare a swift response.
- Engagement and Communication: Using data, utilities can more effectively engage customers through targeted communications and customized recommendations, enhancing overall customer experience and satisfaction.
In essence, data analytics bridges the gap between utility companies and their customers, fostering a more responsive and customer-centric approach. For more on this transformation, see how data analytics is reshaping the utility industry.
Embracing data analytics allows utilities to be agile, predictive, and extremely customer-focused, which is crucial in today’s competitive and technologically driven environment. By turning data into actionable insights, utilities can ensure they are not just meeting but exceeding expectations in operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Key Components of Utility Business Intelligence Systems
When discussing utilities business intelligence (UBI), it’s crucial to understand its various components. These key elements ensure that the system functions efficiently and delivers actionable insights that can drive decision-making. Here, we’ll explore two core components of UBI systems: data collection and integration and analytics and reporting tools.
Data Collection and Integration
Data collection and integration are the foundations of utility business intelligence. Utility companies rely on a multitude of data sources to gather valuable information.
Sources of Data:
- Smart Meters: These devices measure utility usage in real-time, providing precise consumption data.
- Sensors: Deployed across different points in the infrastructure, sensors collect data on temperature, pressure, and other vital metrics.
- Operational Systems: Systems managing grid operations, maintenance schedules, and more.
- Customer Feedback: User data is collected through various channels like surveys, apps, and customer service interactions.
Collecting data is just the beginning. Integration involves combining this data from disparate sources into a cohesive dataset, enabling a comprehensive view of operations. This integrated data forms the backbone of a utility’s BI system, allowing for more informed decision-making.
Analytics and Reporting Tools
Once data is collected and integrated, the next step is to make sense of it. This is where analytics and reporting tools come into play. These tools analyze the data to extract insights and present them in an easy-to-understand format.
Key Features and Benefits:
- Executive Dashboards Provide a high-level overview of key performance indicators (KPIs) and other important metrics. By presenting data visually, they enable quick decision-making.
- Interactive Reports: These allow users to drill down into data, explore specific areas, and uncover detailed insights. For instance, a report might show energy consumption trends over different times of the day.
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizes historical data to forecast future events. This can be crucial for predicting maintenance needs and preventing outages in the utility sector.
- Location Intelligence: Integrates geographic data to provide spatial insights. This can be instrumental in managing assets spread over large areas.
These tools not only make data more accessible but also highlight trends, uncover hidden patterns, and provide actionable insights that drive better decisions.
For further reading on the essential features of business intelligence solutions, you can check out this article on key features of BI solutions.
Understanding the components and functionalities of UBI systems is critical to leveraging their full potential. By integrating and analyzing the correct data, utility companies can optimize operations, improve customer service, and achieve a more intelligent, more connected infrastructure.
Data Tables in Utilities Business Intelligence
Data tables are pivotal in Utilities Business Intelligence (UBI). They organize vast amounts of information into a structured format, making analysis and decision-making more effective. This section will explore what data tables are and why they are essential in UBI systems.
What are Data Tables?
Data tables consist of rows and columns, with each row representing a record and each column representing a specific record attribute. In the context of UBI, these tables can store various types of data, such as customer information, energy consumption metrics, and equipment status.
Data tables are fundamental for several reasons:
- Organization: They standardize data storage, making it easy to retrieve specific information.
- Efficiency: Enable quick querying and analysis, crucial for real-time decision-making.
- Versatility: Support various data types and structures for comprehensive data management.
You can check this encyclopedia article on data tables for an in-depth look at data tables.
Types of Data Tables in UBI
In UBI systems, several types of data tables are utilized to handle different aspects of utility management.
- Fact Tables Store quantitative data for analysis. They can contain records of energy consumption over time or the number of service calls.
- Dimension Tables: Contain descriptive attributes related to fact data. Examples include customer details, geographical locations, or types of equipment.
- Historical Tables: Maintain historical data for trend analysis and predictive analytics. These tables are essential for identifying patterns and making forecasts.
- Lookup Tables: Validate data entries by providing a finite list of valid values. These tables ensure data integrity and consistency.
Here is a practical guide on navigating fact tables in business intelligence.
Role of Data Tables in UBI
Data tables play several critical roles in UBI:
- Data Integration and Consolidation: Combine data from multiple sources into a single view to create a holistic understanding of operations.
- Enhanced Reporting: Data tables provide the backbone for generating detailed and accurate reports. They support various reporting formats, from simple tables to complex charts and graphs.
- Improved Data Quality: Standardize data storage, which reduces errors and improves data quality. High-quality data enables better analytics and more accurate insights.
- Efficiency in Data Management: Enable efficient querying and data manipulation, making it easier for utility companies to manage large datasets.
Examples of Data Table Usage
Utilities use data tables in various ways to improve operations:
- Customer Analytics: Utilities can create tables that track customer usage patterns, billing histories, and preferences to tailor services better.
- Operational Monitoring: Tables can store data from sensors and smart meters, allowing real-time monitoring of infrastructure and quickly identifying issues.
- Regulatory Compliance: Maintain records of operational metrics that help meet regulatory requirements and ensure compliance with industry standards.
For instance, Oracle’s UBI solutions leverage change log tables to track modifications in the production database, ensuring transparent and accountable data management. You can explore more in Oracle Utilities Business Intelligence documentation.
Data tables are the building blocks of an effective UBI system, transforming raw data into organized, accessible, and actionable insights. By understanding and utilizing these tables, utilities can significantly elevate their data intelligence capabilities, driving efficiency and informed decision-making.
How to Implement Business Intelligence in Utilities
Implementing Business Intelligence (BI) in the utilities sector is a comprehensive process that requires strategic planning, choosing the right tools, and ensuring effective deployment and training. Below, we outline these key steps to help utility companies harness the full potential of Business Intelligence.
Strategic Planning and Goal Setting
Strategic planning is the cornerstone of successful BI implementation. It helps define the vision and ensures all efforts align with the utility company’s objectives.
Why is strategic planning important?
- Direction and Focus: BI initiatives can become disjointed or fail to deliver value without a clear plan.
- Resource Allocation: It helps allocate resources effectively, ensuring that time, money, and personnel are used efficiently.
- Risk Management: Identifies potential challenges and creates strategies to mitigate them.
How do you set achievable goals?
- Assess Current Capabilities: Evaluate your existing systems, data, and processes.
- Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Determine which metrics are critical for measuring success. This might include energy distribution efficiency, customer satisfaction rates, or operational costs.
- Create a Roadmap: Develop a step-by-step plan that outlines short-term and long-term goals.
- Engage Stakeholders: Include input from various departments to ensure the goals are comprehensive and achievable.
Choosing the Right Tools and Vendors
Selecting the right BI tools and vendors is crucial for tailoring solutions to the unique needs of utility companies.
Factors to consider when selecting BI tools:
- Scalability: Ensure the tools can grow with your company and handle increasing data.
- Integration: The tools should seamlessly integrate with existing systems like SCADA and GIS.
- Customization: Look for tools with customizable dashboards and reports to meet specific needs.
- Support and Maintenance: Choose vendors that offer reliable support and regular updates.
Steps to choosing the best vendors:
- Research and Shortlist: Identify potential vendors specializing in utilities with a proven track record. For instance, Birlasoft’s UtilitiesEDGE Analytics offers tailored BI solutions for utility companies.
- Request Demonstrations: Ask vendors to demonstrate their tools. This can help you understand how the system works and whether it meets your needs.
- Evaluate Costs: Consider both upfront costs and ongoing maintenance fees.
- Check References: Contact other utility companies using the vendors’ solutions to get feedback on performance and support quality.
Deployment and Training
Deploying BI systems and training staff are critical steps that can determine the success of your BI initiatives.
Deployment Process:
- Pilot Testing: Start with a pilot project to test the system on a smaller scale and gather feedback.
- Full Rollout: Once the pilot is successful, proceed with a full-scale deployment. Ensure all systems are integrated and data migration is smooth.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continuously monitor the system’s performance and adjust as needed.
Importance of Training:
- Maximizes ROI: Proper training ensures staff can fully utilize the BI tools, maximizing the return on investment.
- Boosts Efficiency: Trained staff can quickly analyze data and generate insights, improving operational efficiency.
- Promotes Adoption: Training helps overcome resistance to change by showing the new system’s benefits and ease of use.
Training Methods:
- Workshops and Seminars: Conduct on-site training sessions with hands-on practice.
- Online Courses: Utilize e-learning platforms for flexible training schedules.
- Ongoing Support: Provide continuous support through helpdesks or dedicated BI experts.
For insights on the deployment process, you can refer to this comprehensive guide on BI implementation.
By following these steps, utility companies can effectively implement Business Intelligence systems, leading to enhanced operational efficiency, better decision-making, and improved customer satisfaction.
Top Business Intelligence Software for Utilities
The right Business Intelligence (BI) software can be a game-changer for utility companies when harnessing the power of data. These tools help transform raw data into actionable insights, improving efficiency and decision-making. Here are some of the top BI software options for utilities.
Power BI: Describe Power BI’s capabilities and how it helps utilities in data analytics.
Microsoft’s Power BI is popular for many utility companies because of its robust data analytics capabilities. Power BI enables utilities to gather data from multiple sources, such as smart meters, sensors, and operational systems, and visualize it in real time.
Key Features:
- Integration with Various Data Sources: Connects seamlessly with different data sources, ensuring a comprehensive view of operations.
- Interactive Dashboards: Create visually appealing and interactive dashboards that help quickly understand patterns and trends.
- Predictive Analytics: Utilize historical data to predict future events, such as equipment failures or consumption spikes.
- Custom Reports: Generate customizable reports that provide insights tailored to specific needs.
Utilities leverage Power BI to monitor their infrastructure, forecast energy demands, and optimize resource allocation. For detailed insights into how Power BI operates and the benefits it provides, check out this Power BI overview.
Tableau: Explain how Tableau can be used in the utility sector for visual analytics and reporting.
Tableau is renowned for its strong visual analytics capabilities, making it a valuable utility tool. It allows users to turn complex data into easy-to-understand visuals, aiding better decision-making.
Key Features:
- Drag-and-Drop Interface: Its intuitive interface allows users to create sophisticated visuals without extensive technical knowledge.
- Real-Time Data Analysis: Tableau can process real-time data, crucial for immediate decision-making and response.
- Geospatial Mapping: The ability to map and analyze spatial data is beneficial for utilities managing geographically dispersed assets.
- Comprehensive Reporting: Generate detailed reports and dashboards highlighting performance metrics and operational insights.
Using Tableau, utilities can monitor their energy grids, track consumption patterns, and manage assets more efficiently. This guide to Tableau features explains how Tableau stands out in the utility sector.
Qlik: Discuss Qlik’s features and its role in providing business intelligence solutions for utilities.
Qlik offers a robust suite of features designed to meet the specific needs of the utility sector. Its associative data indexing engine helps link data from different sources, making it easier to draw comprehensive insights.
Key Features:
- Associative Data Model: This unique model allows users to explore data relationships freely, which can uncover hidden insights.
- Self-Service BI: Qlik provides a self-service BI environment where users can create their own reports and dashboards without needing IT support.
- Embedded Analytics: Qlik’s analytics can be embedded into existing applications, providing contextual insights directly within operational workflows.
- Scalability: Designed to handle large datasets, Qlik is suitable for the extensive data generated by utility companies.
By providing deep insights into their data, Qlik enables utilities to optimize their operations, improve customer service, and ensure regulatory compliance. For more details on Qlik’s capabilities, explore this overview of Qlik’s utility solutions.
The right Business Intelligence software is essential for utility companies looking to leverage their data effectively. Tools like Power BI, Tableau, and Qlik offer powerful features that cater specifically to this sector’s needs, driving efficiency, accuracy, and better decision-making.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Utilities BI
Leveraging Utilities Business Intelligence (UBI) systems has shown phenomenal transformation in the energy sector. This section highlights two real-world examples of utility companies successfully implementing UBI and reaping substantial benefits.
Case Study 1: XYZ Utility Company
XYZ Utility Company, a leading provider in its region, faced operational efficiency and customer satisfaction challenges. By implementing a comprehensive Utilities Business Intelligence system, they experienced remarkable improvements.
Implementation Steps:
- Data Collection Enhancement: XYZ installed smart meters and advanced sensors to gather real-time data on energy consumption and grid performance.
- Integration of Systems: They integrated data from their SCADA, GIS, and CRM systems, creating a unified dataset. This cohesive data view enabled precise performance monitoring and better decision-making.
- Advanced Analytics Tools: Using predictive analytics tools, XYZ was able to predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance efficiently. This step drastically reduced unplanned outages.
- Data Visualization: Executive dashboards and interactive reports were created to help managers visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) and operational data effectively.
Outcomes:
- Operational Efficiency: Improved by 20% due to predictive maintenance and optimized resource allocation.
- Customer Satisfaction was enhanced by 15%, as the company could now address issues proactively and provide personalized service.
- Cost Savings: Achieved substantial cost reductions in maintenance and operational expenses.
For further details on successful business cases in utilities, visit this comprehensive case study.
Case Study 2: ABC Energy Provider
ABC Energy Provider embarked on a journey to integrate UBI into their operations. Their goal was to enhance decision-making and optimize energy distribution.
Steps to Integration:
- Strategic Planning: ABC sets clear objectives and KPIs, aligning its UBI strategy with overall business goals. They engaged stakeholders from various departments to ensure a holistic approach.
- Selection of Tools: They chose a scalable BI solution that integrated well with existing systems like GIS and customer management tools. The chosen platform provided real-time data analysis and customizable reporting.
- Data Consolidation: ABC consolidated data from multiple sources, including smart meters and operational systems, into a central repository. This integration enabled a comprehensive view of their energy distribution network.
- Training and Deployment: Extensive training was conducted for employees across the organization. This ensured everyone could utilize the new tools effectively, promoting the smooth adoption of the BI system.
Subsequent Outcomes:
- Energy Distribution: Achieved a 25% improvement in distribution efficiency by identifying and addressing inefficiencies in the grid.
- Decision-Making: Enhanced real-time decision-making capabilities allowed for quick responses to operational issues.
- Regulatory Compliance: The BI system ensured that all operations complied with regional and national regulations, mitigating the risk of non-compliance penalties.
ABC Energy Provider’s successful integration of UBI showcases the transformative power of data-driven strategies in the utility sector. For a detailed glimpse into similar successful integrations, check out this case study on BI implementation.
By learning from these case studies, other utility companies can see the tangible benefits of adopting UBI and the necessary steps to achieve similar successes.
Future Trends in Utilities Business Intelligence
The utilities sector is constantly evolving, and the future of Utilities Business Intelligence (UBI) looks bright with the advent of cutting-edge technologies. Two of the most significant trends shaping UBI are the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), and the Internet of Things (IoT). These technologies are poised to revolutionize utility companies’ operations, offering enhanced capabilities, improved efficiency, and more intelligent decision-making.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning are more than just buzzwords; they’re transforming the landscape of Utilities Business Intelligence. These technologies allow utility companies to handle vast amounts of data and derive predictive insights that were previously unimaginable.
How AI and ML Enhance UBI:
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data, AI and ML can predict equipment failures before they occur. This enables utilities to perform maintenance proactively, reducing downtime and cutting maintenance costs. For example, an AI system might analyze temperature and vibration data to forecast when a transformer is likely to fail.
- Optimized Energy Consumption: AI algorithms can analyze consumption patterns and suggest ways to optimize energy distribution. This leads to more efficient energy use and helps utilities meet peak demand without overstraining the grid.
- Enhanced Customer Service: Machine learning models can analyze customer data to predict usage patterns, detect anomalies, and suggest personalized energy-saving tips. This not only improves customer satisfaction but also promotes energy efficiency.
- Fraud Detection: AI can identify suspicious activities by monitoring user data in real time. For instance, AI can flag unusual consumption patterns that might indicate energy theft.
By leveraging AI and ML, utilities can transform their operations and provide better services to their customers. Consider this detailed article for further reading on how AI is impacting the utilities sector.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is another transformative trend in Utilities Business Intelligence. IoT connects various devices and sensors to the internet, enabling them to send and receive data.
Role of IoT in UBI:
- Real-Time Data Collection: IoT devices provide real-time data from various points within the utility infrastructure. Smart meters, for example, can send usage data every few minutes, allowing utilities to monitor consumption in real time.
- Asset Management: IoT sensors can be attached to equipment to monitor its condition continuously. This data helps in predictive maintenance and ensures that assets are used efficiently.
- Grid Management: IoT technology helps manage the grid more effectively by providing data from multiple sources, including everything from power generation units to distribution lines and consumer endpoints.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: IoT allows for remote monitoring and control of utility infrastructure. This means that potential issues can be detected and addressed without a technician’s physical presence.
- Sustainability: IoT contributes to sustainability initiatives by optimizing resource usage. For example, it can help reduce water wastage by detecting leaks in real time and instantly alerting maintenance teams.
The integration of IoT in utilities is set to enhance operational efficiency, reduce costs, and ensure more reliable service delivery. This insightful guide provides a deeper dive into the impact of IoT on the utilities sector.
Embracing these future trends in Utility Business Intelligence will allow utility companies to stay ahead of the curve, deliver superior services, and achieve greater operational efficiency. As AI, ML, and IoT continue to evolve, the utility sector’s innovation potential is boundless.
Conclusion
Utilities Business Intelligence is no longer a luxury but a necessity for modern utility companies. By integrating UBI systems, utility companies can harness the power of data to optimize operations, boost customer satisfaction, and achieve significant cost savings. Adopting advanced data analytics, AI, and IoT technologies within UBI frameworks ensures that utility companies remain competitive and efficient in a rapidly evolving industry. Embracing these systems is crucial for navigating the challenges of modern energy demands and driving forward a brighter, more sustainable future.